An outbreak of Rocky Mountain spotted fever (RMSF) in southern California has led to three deaths, according to a Dec. 8 health advisory from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).
The total of five reported cases all involved affected people who had recently traveled to or lived in the city of Tecate in Mexico.
All five of the patients had been in Tecate within two weeks of becoming ill.
One patient was an adult, while four were under 18 years of age, the CDC stated in the alert.
Three of the patients lived in the U.S. and two were residents of Mexico.
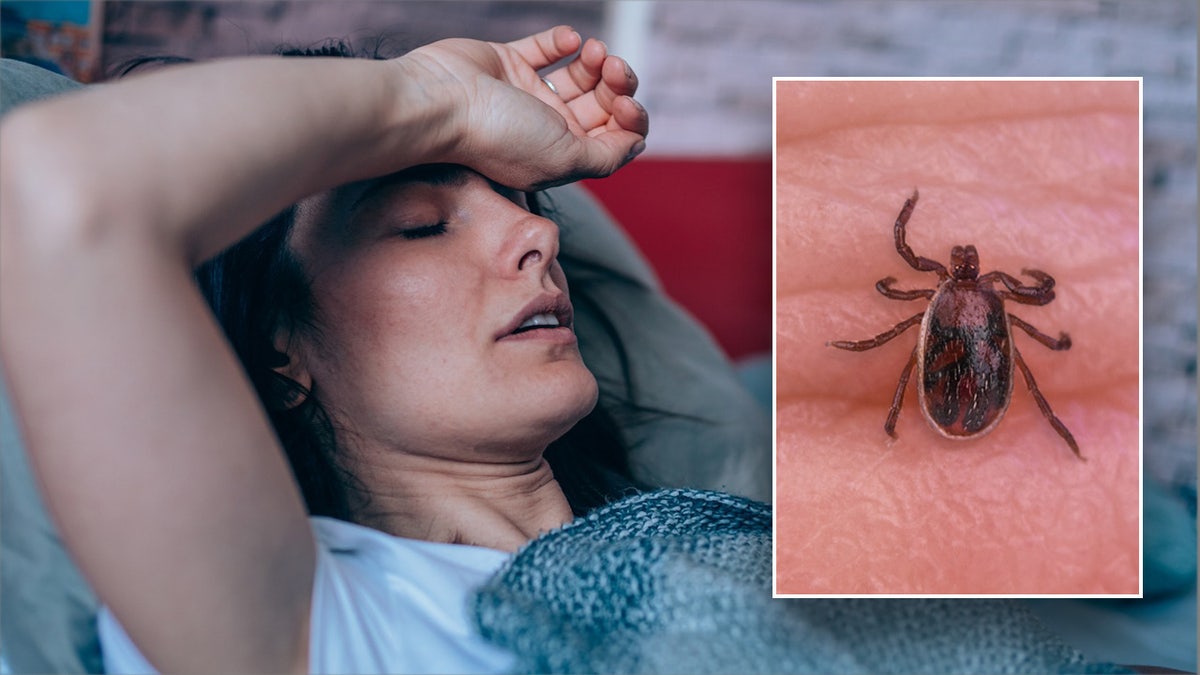
An outbreak of Rocky Mountain spotted fever (RMSF) reported in southern California has led to three deaths, according to a Dec. 8 health advisory from the CDC. (iStock)
Three of these patients died, according to the CDC advisory.
RMSF is a “severe, rapidly progressive and often deadly disease transmitted by the bite of infected ticks,” the CDC stated.
The disease is endemic in several northern Mexico states bordering the U.S., including Baja California, Sonora, Chihuahua, Coahuila and Nuevo León, as well as some parts of the southwestern U.S.
“What’s most interesting about these cases is that they are occurring in Mexico, and I do worry that with our porous borders, these ticks carrying disease could cross [into the U.S.] with migrants.”
The bacteria that cause the fever, Rickettsia rickettsii, are spread by brown dog ticks, which are reddish brown and often found on domestic canines.
“I look for it whenever I am on the lookout for tick-borne diseases, but it is a different tick than Lyme,” said Siegel.
“The dog tick is larger and lacks the characteristic white spot of Lone Star ticks.”
The CDC urges health care providers to consider potential RMSF when evaluating patients with fever who have recently been in northern Mexico.
RMSF is a “rapidly progressive disease” and is often fatal if not treated early, per the CDC.
In Mexico, the disease’s fatality rate can be greater than 40%.
The disease is five times deadlier for young children under the age of 10 compared to adults, the CDC advisory stated.
Despite the disease’s name, not everyone develops the classic “spotted” rash within the first few days.
“The problem is that symptoms are flu-like and somewhat generic, so it can be easily missed,” Siegel warned.
Advanced symptoms can include mental disorientation, coma, swelling in the brain, organ damage, death of body tissue and a decline in respiratory function.
For health care professionals, the CDC calls for all cases to be reported to their local, state, territorial or tribal health departments.


